Key Takeaways
- Accurate property boundaries prevent disputes, delays, and costly legal issues.
- Boundary surveys and title reviews are crucial for ensuring compliant and risk-free site planning.
- Easements have a significant impact on land use, design options, and long-term property value.
- Understanding local laws—such as adverse possession—helps protect property rights.
- Early communication with neighbors and professionals reduces conflicts and improves project outcomes.
Understanding Property Boundaries
For anyone involved in real estate development or land acquisition, understanding property boundaries is fundamental. Property boundaries define the exact dimensions and limits of a land parcel, determining where one ownership ends and another begins. Establishing these boundaries accurately can prevent costly disputes while ensuring adherence to local zoning requirements. An accurate boundary survey, performed by a licensed expert, lays the legal foundation for secure site planning. Working with a reputable civil engineering company can streamline this process and provide essential technical guidance on topographical and jurisdictional challenges.
Failing to identify boundaries clearly can result in encroachments or even lead to legal action between neighbors. It’s important to note that municipal codes and state laws may outline strict protocols for establishing and recording property lines. Homeowners and developers should verify boundaries not only for new projects but also during property transfers, to avoid inherited conflicts or surprises after closing.
The Role of Easements in Site Planning
Easements can significantly affect land use, development, and long-term property value. An easement is a legal right granted to someone else—be it a neighbor, a utility provider, or even the public—to use a defined portion of land for a particular purpose. Unlike ownership transfers, easements set limitations or requirements on your parcel while remaining recorded on the property title or deed. Early identification of any existing easements, through property records or a detailed title search, can safeguard future projects against unexpected constraints.
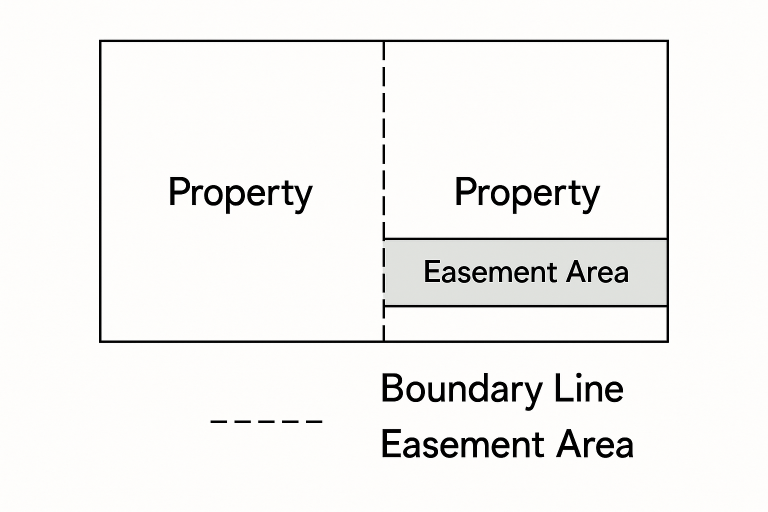
Common Types of Easements
- Utility Easements: Utility companies have the right to install and maintain pipelines, cables, and other infrastructure for water, electricity, or telecommunications services. These are often recorded on subdivision maps and affect future building locations or landscaping plans.
- Access Easements: These provide a legal right of passage through a property, typically for driveways or roads, ensuring that landlocked parcels maintain access to ingress and egress. Failing to respect an access easement can result in litigation or denied building permits.
- Conservation Easements: Used to preserve land, these easements restrict development to protect natural resources, wildlife habitats, or historical sites—sometimes qualifying the property owner for tax benefits or government incentives.
Legal Implications of Easements
Comprehensive knowledge of local and state laws governing easements is crucial to avoid unintended legal issues. For example, in states like Massachusetts, “adverse possession” allows an individual to claim a portion of another’s land if they have used it openly and without the owner’s permission for over 20 years. This highlights the importance of promptly addressing encroachments and monitoring property use. Documentation is key—keep records of communications, boundaries, and property visits over time.
Addressing Property Line Disputes
Disputes can arise when boundaries are unclear or when neighbors disagree about the location of fences, driveways, or buildings. In most cases, the resolution process includes:
- Securing a professional survey to identify the true legal boundary.
- Reviewing property deeds, maps, and any other historical documentation to clarify ownership history and boundary terms.
- Attempting mediation or alternative dispute resolution before escalating to legal proceedings. In complex or high-value disputes, legal intervention may be necessary for a final and binding resolution.
Best Practices for Site Planning
To minimize risk and maximize project success, thoughtful site planning should include:
- Ordering a comprehensive title search to identify all recorded easements, covenants, or restrictions that impact the land.
- Consulting with real estate attorneys and local planning officials to interpret complicated property documents and identify additional regulations that may apply.
- Establishing open channels of communication with neighboring property owners. Early dialogue can often resolve concerns before they escalate into disputes and foster cooperation for shared easements or boundary adjustments.
Final Thoughts
A thorough understanding of property boundaries, easements, and the relevant legal landscape is foundational for successful site planning. By proactively addressing these elements and collaborating with experienced professionals, property owners can avoid costly disputes and ensure their projects comply with all necessary regulations and restrictions, setting the stage for responsible and efficient development.
Also Read-Understanding Spousal Support (Alimony) in Family Law