Messenger RNA (mRNA) technology is rapidly transforming the landscape of vaccine science, providing a versatile and efficient platform to tackle both familiar and new health challenges. In recent years, the world has witnessed the unprecedented speed with which mRNA vaccines addressed the COVID-19 pandemic; now, attention turns to broader possibilities—including promising clinical trials for diseases such as non-small cell lung cancer. If you’re interested in how science is tackling aggressive cancers, this ongoing clinical trial for non small cell lung cancer underscores the expanding reach of mRNA-driven therapeutics. The momentum behind mRNA vaccines signals an era where rapid development, broad adaptability, and targeted immunity become standard features in disease prevention and treatment strategies.
Recent advancements in mRNA technology are being applied beyond infectious diseases to target autoimmune disorders and complex cancers, enhancing immune system responses. Researchers and health organizations are working to address technical challenges in translating laboratory breakthroughs into global health benefits. There is growing investment in mRNA tools, not only for future pandemics but also for innovations in HIV prevention, influenza, and the treatment of rare genetic conditions. Ongoing research is improving the understanding of immune mechanisms and biotechnological delivery, with increased collaboration between public and private sectors aimed at equitable manufacturing and distribution of vaccines globally.
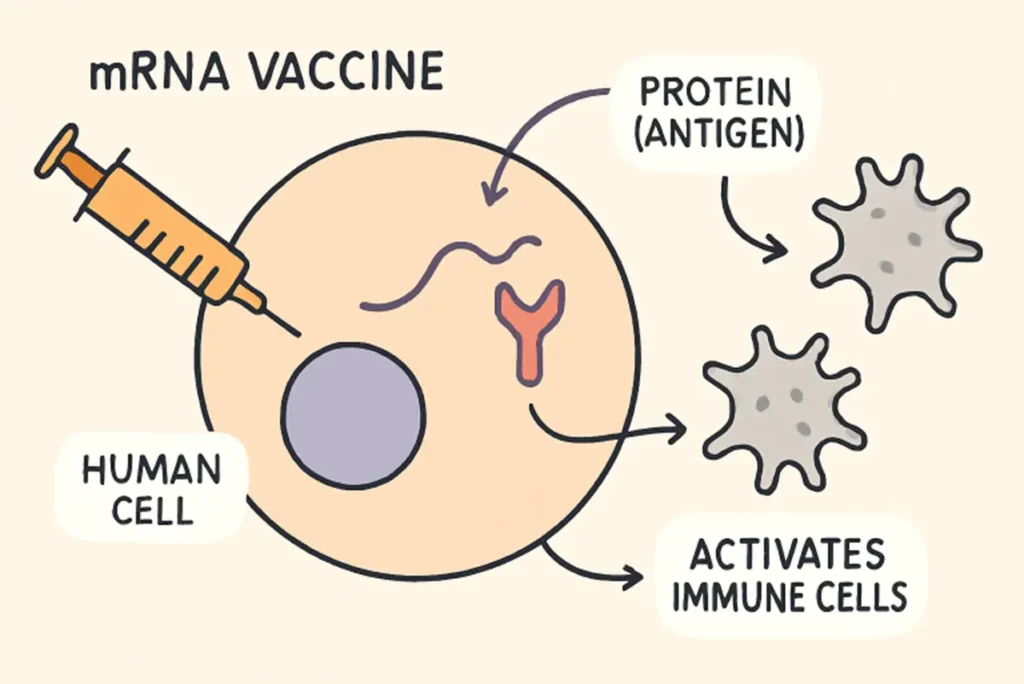
Understanding mRNA Vaccines
Traditional vaccines often require weakened pathogens or parts of a pathogen to train the immune system. In contrast, mRNA vaccines use a genetic blueprint that encodes the antigen—usually a piece of a virus or bacteria—delivered directly into cells. Once inside, the body’s own cellular machinery reads the mRNA instructions to produce the antigen and trigger a strong immune response. This method not only speeds up vaccine development but also enables scientists to adapt quickly as new threats emerge. This approach played a crucial role in the rapid deployment of COVID-19 vaccines during the global emergency.
Advantages of mRNA Vaccine Technology
The benefits of mRNA vaccines go beyond speed. The following highlights their transformative nature:
- Rapid Development: The mRNA sequence can be designed and synthesized in the lab within weeks, offering swift responses during outbreaks.
- Broad Flexibility: Because the mRNA code is easily adapted, scientists can swiftly create vaccines against a wide range of pathogens or even cancer markers.
- Safety Profile: mRNA does not alter DNA or integrate into the genome, and it degrades naturally after use, reducing long-term safety concerns.
Current Applications of mRNA Vaccines
The public first experienced the real-world power of mRNA vaccines during the COVID-19 pandemic. Both the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna vaccines, based on mRNA platforms, demonstrated high efficacy and safety for millions around the globe. However, the scope of their application is rapidly widening. Experimental mRNA vaccines for HIV are showing positive results in early trials, with researchers reporting promising immune responses in participants. In the cancer space, there are exciting efforts focused on personalized vaccines that help the immune system target and destroy tumor tissue. For example, the aforementioned clinical trial for non-small cell lung cancer demonstrates how mRNA’s promise extends to urgent cancer challenges, aiming to revolutionize the future of oncology and targeted therapy.
Advancements in mRNA Vaccine Development
Innovations are continually improving the function and delivery of mRNA vaccines. Researchers at major institutions, such as Yale, are developing methods to modify the structure of mRNA for improved immune activation and broader disease coverage. Enhanced lipid nanoparticles are being engineered for safer and more stable delivery of mRNA payloads to the right cells. These enhancements not only make the vaccines more effective but could eventually allow for single-dose regimens, easier storage, and broader distribution.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the remarkable opportunities mRNA vaccines offer, formidable challenges remain. The requirement for ultra-cold chain storage makes it difficult to distribute these vaccines in remote or underserved regions. Formulation stability and delivery methods must evolve to reduce cold storage dependency and simplify administration—additionally, large-scale manufacturing, cost control, and fair access demand ongoing innovation and international cooperation. Bioethicists and public health experts emphasize the importance of transparent communication to overcome vaccine hesitancy and ensure informed global adoption.
Future Prospects of mRNA Vaccines
Looking ahead, mRNA vaccines are poised to have a tremendous impact far beyond pandemic response. Early-stage research in personalized mRNA cancer vaccines, as well as efforts to develop vaccines for diseases like influenza, Zika, and even rare autoimmune conditions, suggests a future where immunization is not one-size-fits-all but tailored to individual biology and risk. The field is progressing toward more stable formulations that can withstand higher temperatures, potentially solving long-standing distribution challenges. Interdisciplinary collaboration, encompassing molecular biology, nanotechnology, and global health advocacy, will accelerate these innovations. With public and private investment on the rise, breakthroughs in mRNA technology could reshape how the world prepares for—and prevents—disease on a truly global scale.
Conclusion
mRNA technology is ushering in a new chapter for global health, characterized by flexibility, rapid vaccine development, and expanding applications, ranging from infectious diseases to oncology. While challenges exist around stability, equity, and communication, the accelerated pace of research and development points toward a future where mRNA vaccines become foundational tools in medicine. Continued investment and multidisciplinary collaboration are critical to realizing the full benefits of these breakthroughs, ensuring the promise of mRNA reaches populations everywhere.
Also Read-Customer Segmentation Models That Drive Retention in Fintech